Ultrasonography is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows internal body structures to be seen by recording echoes or reflections of ultrasonic waves. Unlike X-rays, which are potentially dangerous, ultrasound waves are considered to be safe.
Ultrasound equipment directs a narrow beam of high frequency sound waves into the area of interest. The sound waves may be transmitted through, reflected or absorbed by the tissues that they encounter.
“Ultrasound waves that are reflected will return as “echoes” to the probe, and are converted into an image.”
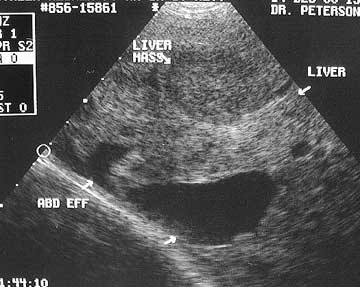
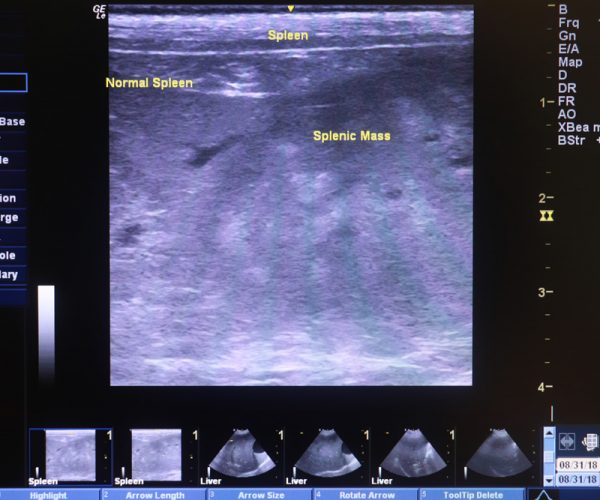
This gives a 2-dimensional “picture” of the tissues under examination. The technique is invaluable for the examination of internal organs and was first used in veterinary medicine for pregnancy diagnosis. However, the technique is also extremely useful in evaluating heart conditions, identifying changes in abdominal organs, evaluating fluid in the chest and abdomen, and diagnosis of cysts and tumours.
Will my dog have to have an anesthetic?
Mild anesthesia may or may not be needed for ultrasound examinations. The technique is painless and most animals will lie comfortably while the scan is being performed, but fractious, frightened, and uncomfortable animals will likely need sedation. Image quality is also improved with sedation since breathing stabilizes, your pet is relaxed, and panting is accounted for.
When will I know the results of the examination?
Since an ultrasound study is performed in real time, the results of what is seen are known immediately. In some cases, the ultrasound images may be sent to a veterinary radiologist for further consultation. When this occurs, the final report may not be available for a few days. A comprehensive ultrasound commonly takes 15-30 minutes on average.
We primarily use ultrasonography for scanning the abdomen. It is the ideal tool for imaging the liver, spleen, intestines, kidneys, and bladder. Primarily used in emergencies to assess fluid/blood and masses in the abdomen or thorax, it also is used for routine procedures such as obtaining urine from the bladder by ultrasound-guided cystocentesis.